Optimizing SQL databases is critical for ensuring speed and efficiency, especially in large-scale projects.
In this guide, I’ll explore the most effective optimization techniques for popular databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL.
1️⃣ Using Indexes
Indexes help speed up data retrieval, especially in WHERE and JOIN queries.
Creating an index:
CREATE INDEX idx_username ON users(username);Listing indexes:
SHOW INDEX FROM users; -- MySQL
SELECT * FROM pg_indexes WHERE tablename = 'users'; -- PostgreSQLBenefits of indexes:
- Increases query speed
- Speeds up JOIN operations
- Improves performance in ORDER BY
Note: Unnecessary indexes can consume storage and slow down INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE operations.
2️⃣ Query Optimization
Use these techniques to write efficient SQL queries:
Using EXPLAIN ANALYZE to review query plans:
EXPLAIN ANALYZE SELECT * FROM orders WHERE status = 'completed';Using subqueries instead of JOIN (in some cases):
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id IN (SELECT user_id FROM orders WHERE amount > 1000);Using LIMIT to fetch only needed rows:
SELECT * FROM products ORDER BY price DESC LIMIT 10;3️⃣ Normalization vs. Denormalization
Normalization: Ensures consistency by reducing data redundancy.
Denormalization: Allows redundancy to simplify complex queries.
Example – Normalized:
CREATE TABLE orders (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id INT,
product_id INT,
quantity INT
);Example – Denormalized:
ALTER TABLE orders ADD COLUMN customer_name TEXT;4️⃣ Using Caching
Tools like Memcached or Redis can cache frequently used queries.
Example – Redis caching with PHP:
$redis = new Redis();
$redis->connect('127.0.0.1', 6379);
$cacheKey = 'top_products';
if (!$data = $redis->get($cacheKey)) {
$data = $db->query('SELECT * FROM products ORDER BY sales DESC LIMIT 10')->fetchAll();
$redis->setex($cacheKey, 3600, json_encode($data));
}Materialized Views in PostgreSQL:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW top_sellers AS
SELECT product_id, COUNT(*) as total_sales FROM orders GROUP BY product_id;5️⃣ Using Connection Pooling
PgBouncer for PostgreSQL and ProxySQL for MySQL help manage database connections efficiently.
Example – PgBouncer configuration:
[databases]
db1 = host=127.0.0.1 port=5432 dbname=mydatabase6️⃣ Database Configuration Tuning
InnoDB Buffer Pool setting in MySQL:
[mysqld]
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 2GWork Mem setting in PostgreSQL:
work_mem = 64MBThese settings help large queries use RAM more efficiently, reducing disk access.
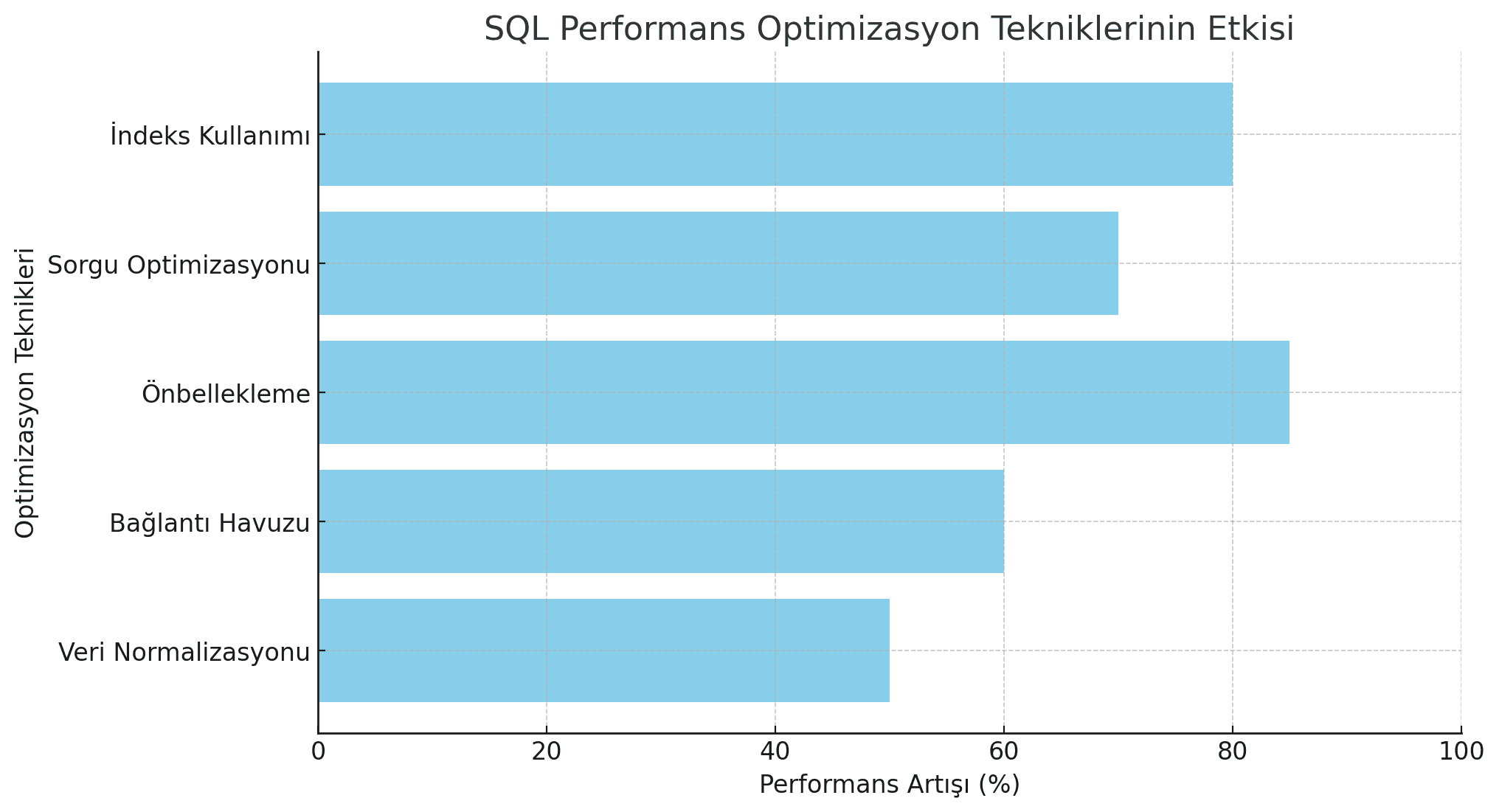
To achieve high performance in SQL databases:
- Use proper indexing
- Test queries with EXPLAIN ANALYZE
- Utilize caching systems
- Balance load with connection pooling
- Optimize database configurations
By applying these techniques, you can reduce query times from seconds to milliseconds!
Related Articles